High-Performance Hot Forging
Solutions for Custom Metal Parts
Delivering durable, high-strength components with precision and reliability for industries
like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
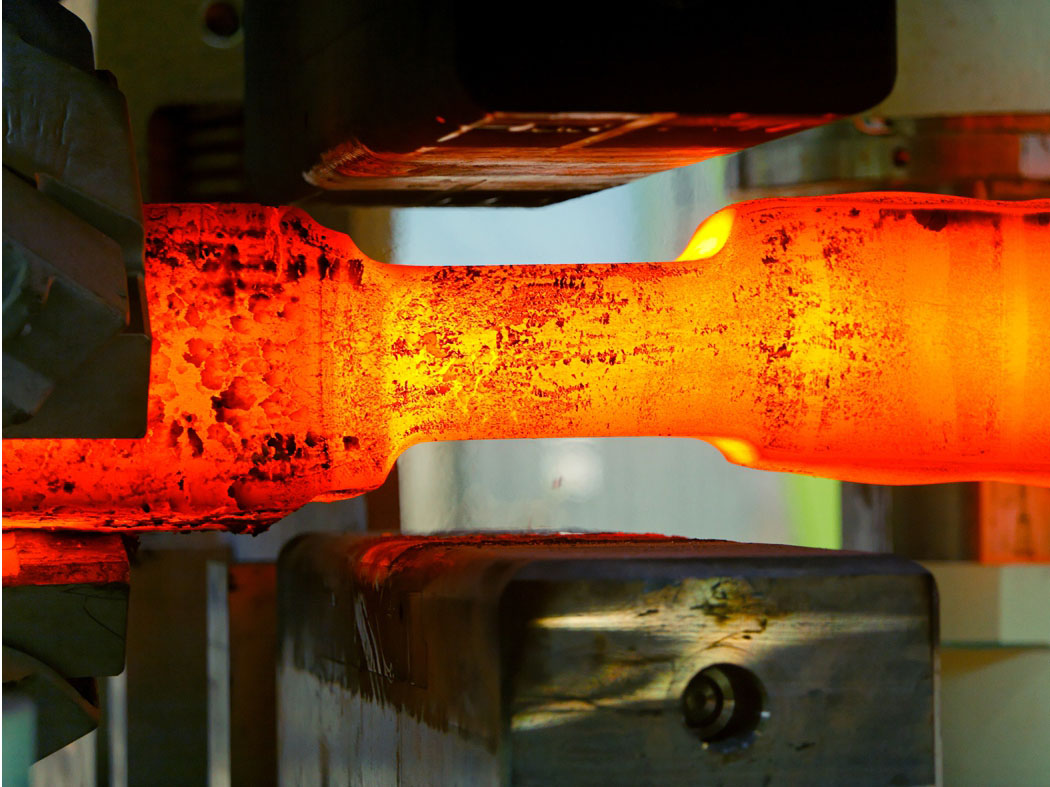
What is Hot Forging?
Hot forging is a process in which metals are heated to a high temperature and then plastically deformed by mechanical forces. This process is suitable for most metallic materials, especially in applications where strength, toughness and fatigue resistance need to be improved, such as automotive parts, aerospace components, engineering machinery parts, etc.
The global forging market is expected to reach $150 billion by 2027, with hot forging accounting for 60% of the market share.

Hot Forging Process Explained
Forging is a manufacturing process in which metal is pressed, hammered or extruded under great pressure to form high-strength components, known as forgings.
The process is usually carried out in the hot state, i.e., the metal is preheated to the desired temperature before processing. It is important to note that the forging process is completely different from the casting process, as the metal used to make forged parts is not melted and poured as in the casting process.
Investment Casting Process Flowchart
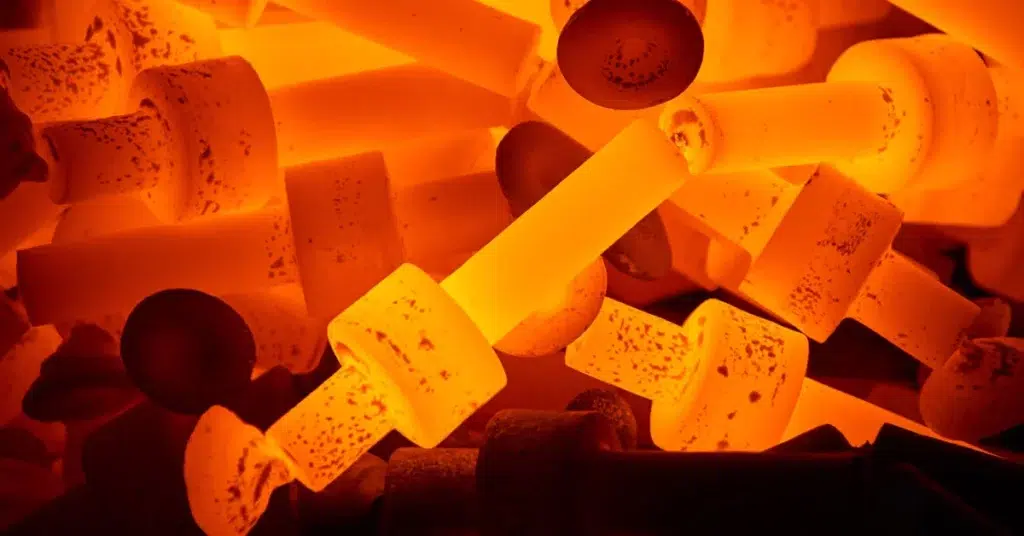
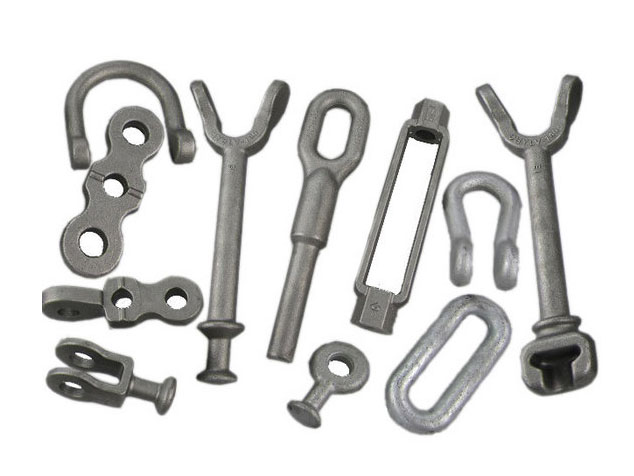
Typical Products Manufactured Using Hot Forging
Our hot forging solutions can achieve material strengths up to 200,000 psi, ideal for heavy-duty and high-stress applications.
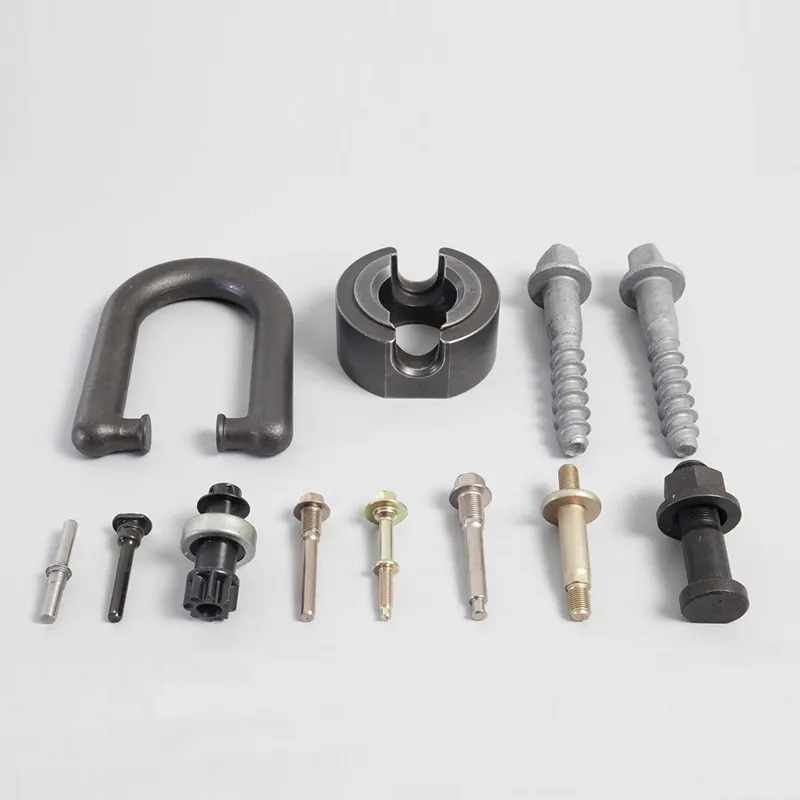

Mechanical fixing fittings
Material: Aluminum, Steel, Alloy
Treatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc
Application: Transportation equipment
inquiry nowTreatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc
Application: Transportation equipment

Transport Anchor For Precast Concrete
Material: Aluminum, Steel, Alloy
Treatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc
Application: building construction
inquiry nowTreatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc
Application: building construction

Connecting rods
Material: Aluminum, Steel, Alloy
Treatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc.
Application: Automotive, Mechanical Engineering
inquiry nowTreatment: Painting, Sand Blasting, Electroplating, etc.
Application: Automotive, Mechanical Engineering

Electricity Accessories
Material: Aluminum, Steel, Alloy
Treatment: sandblast
Application: Electricity industry
inquiry nowTreatment: sandblast
Application: Electricity industry
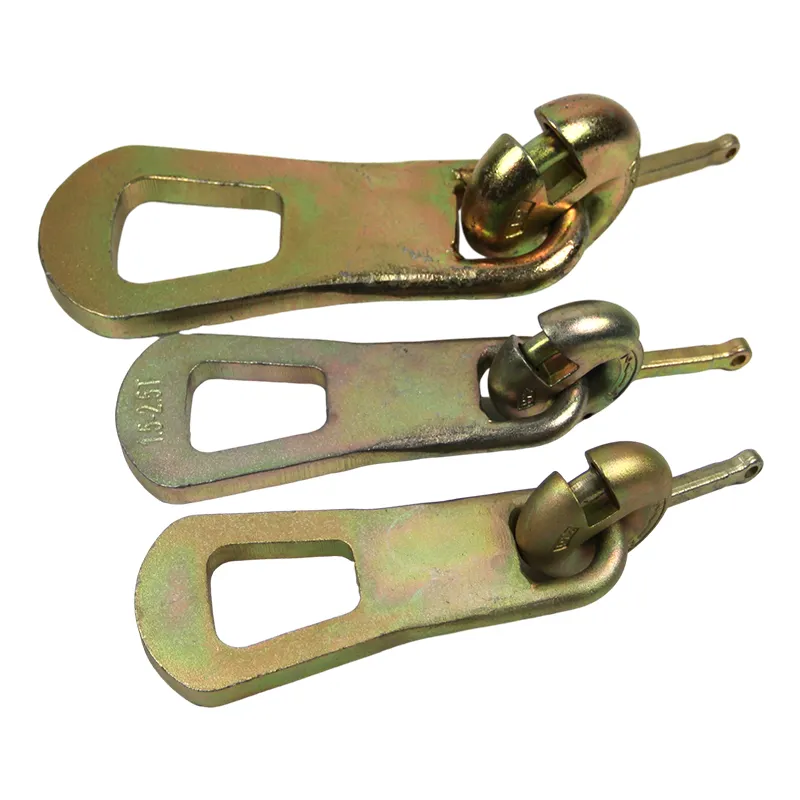


Concrete lifting clutches
Material: alloy steel
Treatment: galvanized zinc
Application: building construction
inquiry nowTreatment: galvanized zinc
Application: building construction
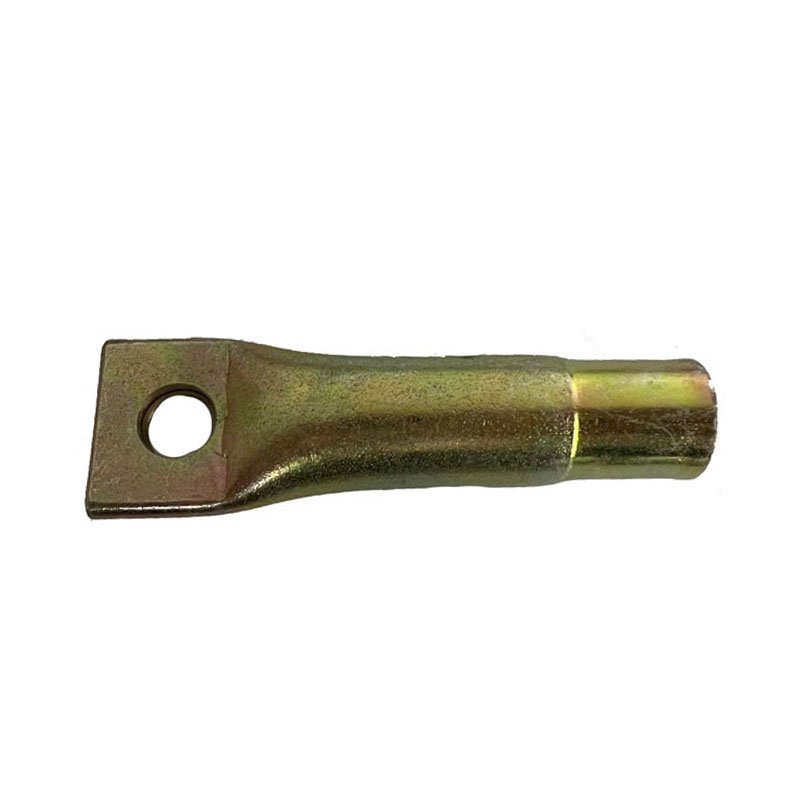

Precast Concrete Lifting Socket Insert
Material: alloy steel
Treatment: galvanized zinc
Application: building construction
inquiry nowTreatment: galvanized zinc
Application: building construction

Valve Bracket
Material: Stainless Steel
Treatment: Plating, Painting, Powder Coating
Application: petrochemicals
inquiry nowTreatment: Plating, Painting, Powder Coating
Application: petrochemicals
Material
Ferr can meet material specification according to ASTM, SAE, AISI, ACI, DIN, EN, ISO, GB standards.
stainless steels
| austenitic stainless steel |
|---|
| 304: good corrosion resistance |
| 316: higher corrosion resistance |
| 321: with Ti |
| 310s: Excellent high temperature performance |
| ferritic stainless steel |
|---|
| 430:Commonly used ferrite models |
| 409: heat-resistant |
| 439: Weldability better than 430 |
| 200 Series |
| martensitic stainless steel |
|---|
| 410: good mechanical properties |
| 420: High hardness, cutting grade |
| 440C: Excellent hardness and wear resistance |
| 100 Series |
| Precipitation hardening stainless steel |
|---|
| 17-4PH: High mechanical strength and good corrosion resistance |
| 15-5PH: Better toughness |
| 500 Series |
| Duplex stainless steel |
|---|
| 2205: High corrosion resistance |
| 2507: Super duplex stainless steel for harsh environments |
| 400 Series |
alloy steel
| Low Alloy Steel |
|---|
| 16Mn:High manganese content |
| Q345:Small amount of MnSi |
| 20CrMnTi:Contains chromium, manganese and titanium, high hardness |
| AISI 4130:Contains chromium-molybdenum, good toughness |
| AISI 4140:Excellent heat treatment performance |
| Copper Alloys |
|---|
| H62:62% copper for good plasticity and corrosion resistance |
| H68:68% copper for high conductivity |
| ZCuSn10:Contains about 10% tin, good corrosion and wear resistance. |
| ZCuAl9Mn2:Aluminum bronze for wear and impact resistance |
| B10:10% nickel for seawater corrosion resistance |
| B30:30% nickel for higher temperature resistance |
| Aluminum Alloys |
|---|
| 6061:Contains magnesium and silicon for high strength and corrosion resistance |
| 7075:Contains zinc-magnesium-copper for extreme strength |
| A356:High silicon content, good casting performance |
| ZL101:High heat resistance, low density |
| Superalloys |
|---|
| Inconel 718:Containing nickel-chromium, high temperature resistance, strong oxidation resistance |
| Hastelloy C-276:Contains nickel, molybdenum and chromium for excellent corrosion resistance |
| Haynes 25:Containing cobalt-nickel-chromium, with high resistance to oxidation and creep. |
| Stellite 6:Contains cobalt-chromium tungsten, resistant to wear and corrosion |
| A-286:Containing iron-nickel-chromium-molybdenum-titanium, good overall performance |
| Alloy 800:Containing FeNiCr, high temperature and corrosion resistant |
carbon steel
| mild steel |
|---|
| Q195:Good plasticity and workability |
| Q235:Moderate strength, excellent toughness |
| A36:Good weldability, good low temperature performance |
| medium carbon steel |
|---|
| 45#:High hardness and good wear resistance after tempering |
| 40Mn:High strength and excellent toughness |
| AISI 1045:Excellent overall performance after tempering |
| high carbon steel |
|---|
| T8:High hardness, good wear resistance |
| T10:suitable for cold work molds |
| AISI 1095:Very high hardness and wear resistance |
Let’s talk about your next project !
Whether you have detailed drawings or just a concept, we’re ready to listen.
I don't have complete drawings, can I send inquiry?
Yes, we can help you analyze based on your description, samples and photos.
I am not sure if you can do my parts?
Most of our customers come to us because “others say they can’t do it”.
Are you a factory or a trader?
We are a factory and have a project management team that can handle the technology, cost and delivery at the same time.